前言
之前关于 hadoop,也就试过一个 wordcount,这次来学习一下用 mapreduce 实现矩阵乘法,体会一下里面的思路过程。
预备
开发环境准备
第一次开发 MapReduce 程序可以看下这边的环境准备
开发环境准备
MapReduce
关于 MapReduce 这边只用到最基础的,因此了解一下wordcount也就能知道最基础的思想。
- Map 将每行数据转为 key,value 的格式;
- shuffle 会将相同 key 的 value 放到一个数组迭代器里变为 key,values[];
- Reduce 读取数据并做计算处理;
数据存储
因为针对的是稀疏的大矩阵,直接按矩阵格式存储会产生很多 0,
因此这边采用了 x, y ,v 的格式,x,y 表示坐标(从 0,0 开始),v 表示数值
测试数据
为了方便这边就用 int 的数据来测试,且只准备了一个小矩阵,但原理一样
1 | // matA 4x3 |
转为 x, y, v 的格式后
1 | // matA |
将两个文件存到项目根目录/input 下
三种实现
这边要讨论三种实现,思想上稍稍不同。
下面矩阵名以 A,B,C 替代,表示 AxB=C。
A 为 mxl
B 为 lxn
C 为 mxn
基础的矩阵相乘
关于矩阵相乘,一般的就会考虑到 A 的行点乘以 B 的列为 C 的一个值,
所以最先考虑的是将 A 的第 i 行和 B 的第 i 列的数据放到一个 mapreduce 的 key 中,key 值为计算结果在 C 中的坐标。
然后考虑 A 的每行数据需要在 B 的每列用到,用到的地方都需要拷贝一份数据到对应 key 中,B 同样,就是 map 部分逻辑。
例如 A 的第一格数据 0,0,1,他会在与 B 的第一列,第二列点乘的时候用到成为 C 的第一行的一部分,就将它加到 key(0,0)(0,1)中。
例如上面的测试数据,这么做以后得到的 key,value 为,就是 map 部分
value 的第一个区分矩阵,第二个是 A 的列\B 的行,第三个表示值。
1 | 0,0 |
在 reduce 阶段,将 A 的列与 B 的行相等的计算乘积并相加的到 C 的一格的结果。
盗一张图,可以很清楚的表示这个过程,他这个的定义 1,1 为开始点
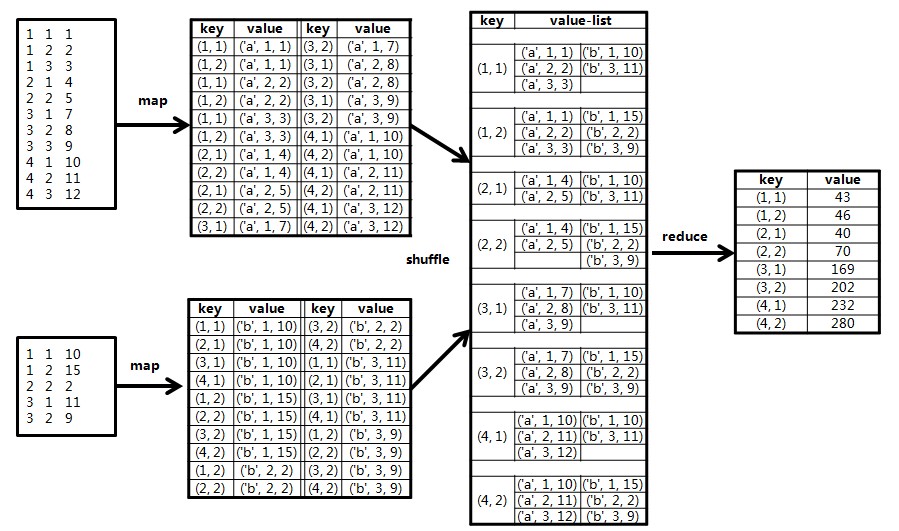
来看具体代码
1 | package cn.ganjiacheng; |
分块矩阵乘法
上面的方法有个问题是在 Map 过程中 A 的每个数据要扩大 B 列倍,B 的每个数据要扩大 A 行倍,数据较为冗余。
一种优化方式是将矩阵分块。
分块的计算原理如下
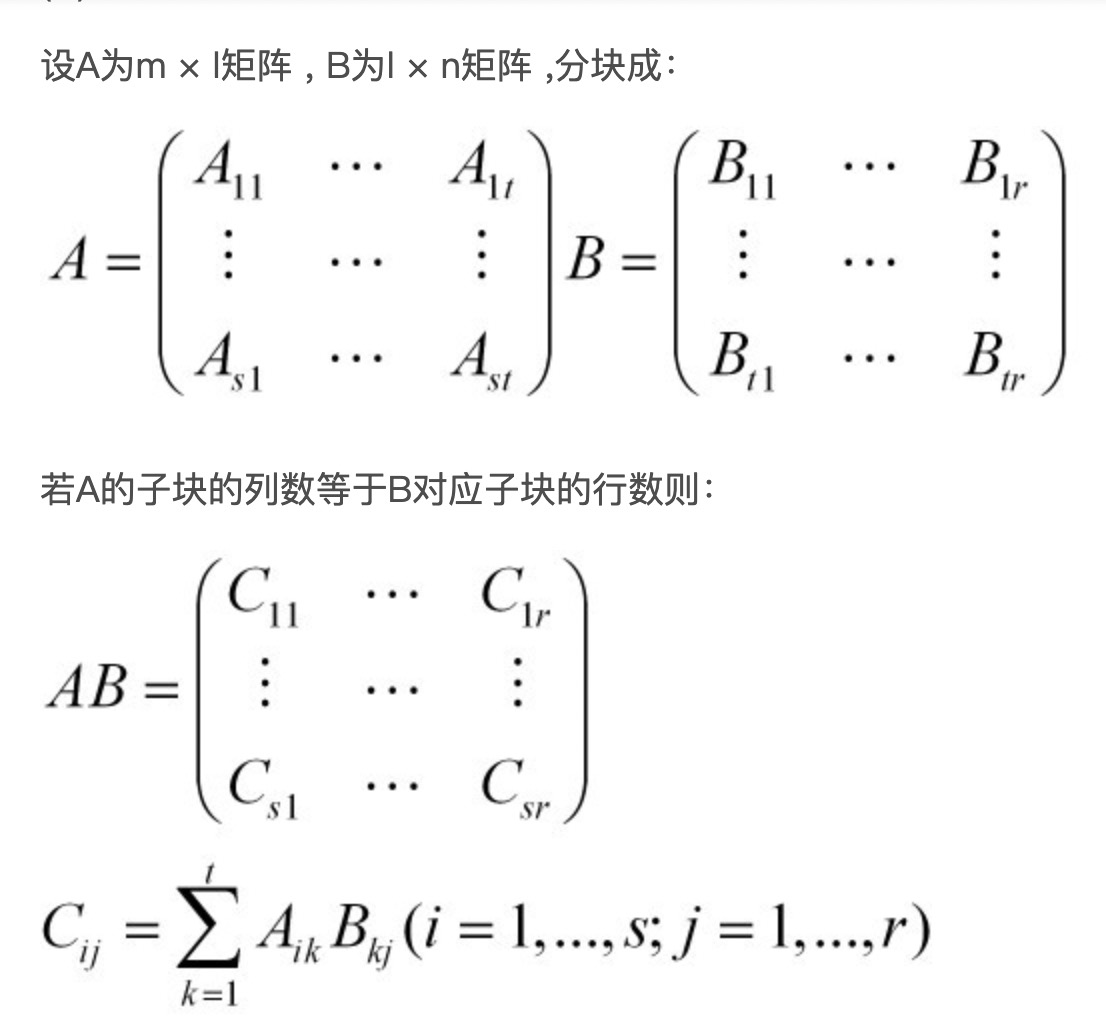
分块后如果是 k 个分为一块,数据大致可以减少 k 倍,
map 的时候按 C 的结果大块进行取 key,同时将需要进行对应计算的 A 列块和 B 行块划分到一起,reduce 的时候进行对应的块的矩阵计算。
这边举例以 2 个为一块,矩阵切分后如下,A 为 2x2,B 为 2x1
C 即为 2x1,shuffle 后的的 key 原本会有 6 个,现在只需要 4 个,且每个数量也减少了
如下将 1 2 4 5 和 10 15 0 2 (DIV *_ 2 _ 2)的块划到一起并在第一层 reduce 做计算,返回的 key 为对应行列
然后第二层 mapreduce 将计算结果合并累加
1 | 1 2 | 3 |
上代码
1 | package cn.ganjiacheng; |
列行相乘
这个的思想基本和第二种的 reduce 部分差不多,但这个不是利用 hashmap 来自己合并,而用两次 mapreduce 来实现。找到 A 的列与 B 的行值相等的两个值进行乘积作为值,取 A 的行与 B 的列作为 Key,然后将同样 key 的 value 相加就可以得到结果。
这个需要分两步 MapReduce,
第一步 Mapreduce 是取相等的列行相乘得值,key 为对应的行列
第二步 MapReduce 是将相等的 key 相加,得到 C 的结果。
1 | package cn.ganjiacheng; |
小结
- 第一种基本的矩阵乘法,实现比较直接,主要问题在于 map 的时候数据复制了 n 份,导致 shuffle 的数据过大;另一个是每个 reduce 的时候获得的数据量为 m+n,且需要转存到内存中,可能会导致存储不下。
- 第二种分块相乘,将数据复制分数减少了 DIV 倍,同时一个 reduce 的数据量在 DIV*_2 _ 2 的大小;麻烦的是需要控制的就是 DIV 取合适的值。
- 第三种列行相乘,这边实现的是直接在全集上进行列行分,其实也可以在分块后进行列行,这边的每个 reduce 也是会有 m+n 的数据进来内存中,分块后再按列行划分就是步骤会多了点,也是可以的。
感觉最为关键的一步是在 map 的时候对数据进行合理的计算划分与分发,就如同这边对矩阵的分块/列行对应分发(什么作为 key),不同的 key 划分对应的计算量和中间过程数据完全不同。划分完后的每块 reduce 的计算基本是水到渠成的事情,都是一些累加或点乘的事情。
MapReduce 开发环境
这边因为本地装的 hadoop2.7.3 版本,
因此新建 maven 项目,使用了 2.7.3 的依赖包,不过运行可以不依赖本地
1 | <dependency> |
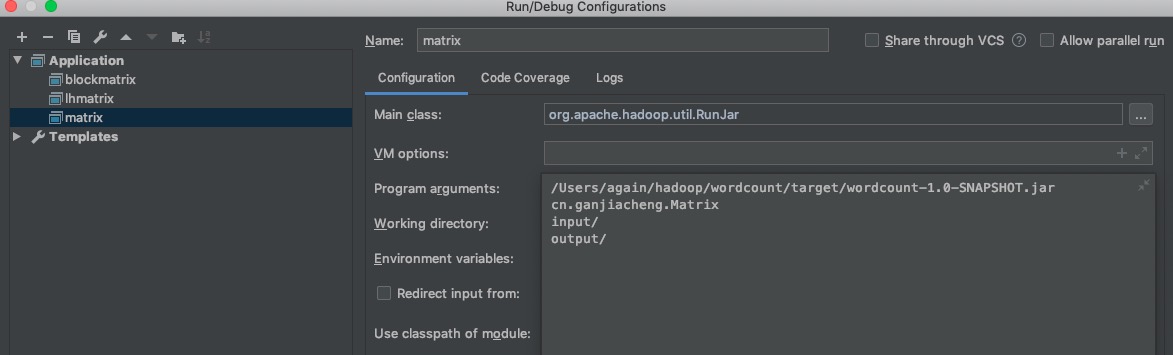
打开 idea 的运行配置,
新建 Application 的配置,
Main class 填写如下;
arguments 参数填写如下,第一个为 mvn 打包后的 jar,
第二个为运行的类,
后面两个为类的参数,表示输入输出路径(这边相对路径是相对项目根目录)
然后直接点运行即可,debug 也可以
感谢
赞赏一下
 支付宝打赏
支付宝打赏 微信打赏
微信打赏